In this article, we will introduce the relevant knowledge of the network, especially the network standard of Ethernet , so that you can understand why all computers can be connected behind the scenes.

The role of the network
The network enables two computers to send and receive information to each other. We are not always aware of our frequent access to information on the Internet. The Internet is arguably the most prominent example of a computer network. It connects millions of computers in the world, but it is often smaller networks that play a role in our daily access to information. Many public libraries have replaced their card catalogs with computer terminals, and readers can search for books faster and easier. The airport is equipped with numerous display screens to inform passengers of arrival and departure flights. Many retail stores also use dedicated computers to handle POS transactions. In the above cases, it is the network that connects different devices located in multiple locations together so that people can access a shared database.
Before introducing the details of network standards such as Ethernet, we must first understand some basic terms and their explanations. They describe different network technologies and their differences-let ’s start!
LAN and WAN
We can divide the network technology into one of the following two basic technologies: Local Area Network (LAN) technology, which can connect many devices together at a relatively close distance (usually in the same building). The terminal computer used to display the book information in the library can be connected to the local area network. Wide area network (WAN) technology can connect devices tens of kilometers apart, but the number of devices that can be connected is small. For example, if two libraries at both ends of the city want to share book catalog information, they can use WAN technology to connect, which may require the lease of a dedicated line from a local telephone company to exclusively transfer their data.
Compared with WAN, LAN is faster and more reliable, but the continuous development of technology has made the boundaries between them more and more blurred. With the help of optical fiber, LAN technology can be used to connect devices that are tens of kilometers away, while greatly improving the speed and reliability of the WAN.
Ethernet
In 1973, Bob Metcalfe, a researcher at Xerox's Palo Alto Research Center (commonly known as PARC), designed and tested the first Ethernet network. At that time, this network connected Xerox's "Alto" computer to a printer, and Metcalfe developed a physical method of cable connection for connecting devices on the Ethernet, as well as a standard for controlling data transmission on the cable. Now, Ethernet has become the most popular and widely used network technology in the world. Many problems involved in Ethernet are also problems to be solved by many other network technologies. Understanding the methods of Ethernet to solve these problems can help you improve your overall understanding of the network.
With the increasing maturity of computer networks, the Ethernet standard is constantly developing some new technologies, but the current operating mechanism of all Ethernet networks is still derived from the original design of Metcalfe. In the original Ethernet, all devices on the network shared a single cable for communication. When the device is connected to the cable, it can communicate with other connected devices. In this way, the network can be expanded to accommodate new devices without any modification to existing devices on the network.
Basic knowledge of Ethernet
Ethernet is a local area network technology. The network is generally distributed in a building, and the connected devices are usually close. The cable between Ethernet devices is up to several hundred meters long, so it is not suitable for connecting multiple geographically dispersed locations. However, the advancement of modern technology has greatly improved the connection distance of Ethernet. Today, people have been able to build Ethernet networks that are tens of kilometers away.
protocol
For network connections, the term protocol refers to a set of rules used to control communications. The meaning of a protocol to a computer is just like the meaning of language to humans. Since this article is written in Chinese, you must be able to read and understand Chinese to understand the content of the article. Similarly, for two devices on the network to successfully communicate, they must both understand the same protocol.
Ethernet terminology
Ethernet follows a set of simple rules that control its basic operations. To better understand these rules, it is important to understand basic Ethernet terminology.
Media-Ethernet devices are connected to a common medium, which provides a path for the transmission of electrical signals. Historically, coaxial copper cables have been used as transmission media, but currently twisted pair or fiber optics are more common.
Network segment-We call a single shared medium an Ethernet segment.
Node—The equipment connected to the network segment is called a site or node.
Frames-Nodes use short messages called frames to communicate. Frames are information blocks of variable size.
Frames are similar to sentences in human language. In Chinese, we have some rules when constructing sentences. For example, each sentence must contain a subject and a predicate. The Ethernet protocol also specifies a set of rules for constructing frames. The maximum and minimum lengths of the frame are clearly defined, and the frame must contain a set of necessary pieces of information. For example, each frame must include a destination address and a source address, which indicate the receiver and sender of the message, respectively. A unique node can be identified by address, just as a person can be found by name. No two Ethernet devices should have the same address.
Since the signal on the Ethernet medium can reach all connected nodes, the target address is crucial for identifying the target receiver of the frame.
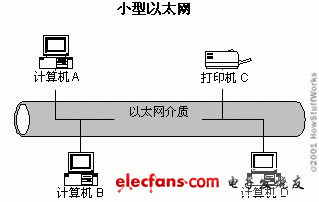
For example, in the above figure, if computer B sends data to printer C, computers A and D can also receive and view frames. However, after the station receives the frame, it will first check the frame's destination address to see if the frame was sent to itself. If not, the site will discard the frame without viewing its contents.
One interesting thing about the Ethernet address is that it has a broadcast address. If the target address of the frame is a broadcast address (referred to as a broadcast for short), it means that it is sent to all nodes on the network, so each node will receive and process this type of frame.
What does CSMA / CD in Ethernet mean?
"CSMA / CD" means Carrier Sense Multiple Access with collision detection, which describes the Ethernet protocol to control the communication between nodes. The word seems a bit complicated, but if we break it down into a few small concepts, we will find that the rules it describes are very similar to the rules that people use when conducting polite conversations. To help describe the operation of Ethernet, we use the dialogue on the dinner table as an analogy.
We represent the Ethernet segment as a dining table, and let a few representatives of the nodes sit at the dining table to talk politely. The term multiple access covers what we discussed above: when transmitting data on an Ethernet site, all sites on the media will hear the transmission behavior, just like when a person at the dinner table is talking, everyone can hear His (her) speech is the same.
Now, suppose you are also sitting at the table and have something to say. However, I was talking at the time. Since this is a very polite conversation, you should not speak immediately and interrupt others, but wait until I finish speaking. The situation just described is called carrier sensing in the Ethernet protocol. Before a site starts transmitting data, it will "listen" to the media to determine whether other sites are transmitting. If the media is quiet, the site considers it to be a suitable time to transfer data.
 
| About Glass Fiber Covered Flat Copper Wire |
Fiber Glass Covered Aluminum/Copper Wire is according to customers` requirement, aluminum/Copper conductor is evenly covered with one or two layers of non-alkali fiberglass, then it`s impregnated in compatible insulating coating of required thermal class baked to make a whole between fiberglass and aluminum/Copper conductor
Excellent resistance to abrasion and solvent, excellent electricity

a) Excellent resistance to abrasion and solvent,
b) Excellent electricity performance
c) Excellent heat shock, adherence and flexibility,
d) High cut through
e) Resistance to high voltage in oil;
f) Rise up the filling coefficient of the transformer;
g) Reduce volume and the cost of the transformer
Glass Fiber Covered Flat Copper Wire
Glass Covered Winding Wire,Glass Fiber Covered Flat Copper Wire,Fiber Glass Covered Copper Wire,Generator Flat Glass Fiber Covered
HENAN HUAYANG ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY GROUP CO.,LTD , https://www.huaonwire.com