Binocular vision ADAS chip - S32V234
The S32V234 uses four ARM Cortex A53s as core CPUs for higher performance-to-power ratios. An ARM Cortex M4 is used as an on-chip MCU for real-time control of critical IOs such as CAN-FD and supports the AutoSAR operating system. The chip contains a programmable image signal processor (ISP), so the matching image sensor can output raw data, which reduces material costs and saves space.
In addition, the chip also contains two visual acceleration engines called APEX2CL. Each APEX2CL has 64 local computing units (CUs) with local memory and dedicated DMA to accelerate the image recognition process via SIMD/MIMD (Single Instruction Multiple Data/Multiple Instruction Multiple Data).

   It is also worth noting that, considering the stringent requirements of the ADAS system for safety and reliability, the S32V234 incorporates such things as ECC (Error Checking and Correction), FCCU (Fault Collection and Control Unit), M/L BIST (design). A variety of security mechanisms, such as memory/logic built-in self-test, can meet the requirements of ISO26262 ASIL B~C.
The advantages of binocular vision ADAS
Compared to monocular vision, the key difference between Stereo Vision is that dual cameras can be used to image the same target from different angles to obtain disparity information and estimate the target distance. Specific to visual ADAS applications, if a monocular camera is used, in order to identify targets such as pedestrians and vehicles, large-scale data acquisition and training are usually required to complete the machine learning algorithm, and it is difficult to identify irregular objects; Although the accuracy of the laser radar for ranging is high, the cost and difficulty are also high.
The biggest advantage of binocular vision is to achieve target recognition and ranging with certain accuracy under the premise of low development cost, and complete ADAS functions such as FCW (forward collision warning).
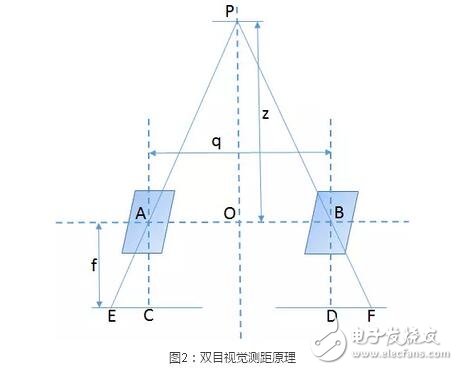
The basic principle of binocular vision ranging is shown in Fig. 2: the parallax of the target point P in the two cameras is d=EC+DF, and the derived distance z=(fq)/d is derived according to the similarity of the triangles. The focal length f and the camera optical axis distance q can be regarded as fixed parameters, so that the distance z can be obtained by obtaining the parallax signal d.
Binocular vision ranging step
Camera calibration
Image acquisition
Image preprocessing
Feature extraction and stereo matching
3D reconstruction
Among them, the camera calibration is to obtain the camera's internal and external parameters and distortion coefficients, etc., which can be performed offline; the synchronization of left and right camera image acquisition, the quality and consistency of image preprocessing, and stereo matching (acquisition of disparity information) and 3D reconstruction (Acquisition of distance information) The huge computational complexity of the algorithm's real-time requirements poses a challenge to implementing binocular vision ADAS on embedded platforms.
Magnetoelectric Proximity Switch
The magnetic proximity switch is a kind of proximity switch. The magnetic proximity switch is one of many types in the sensor family. It is made by the use of electromagnetic working principle and advanced technology. It is a position sensor. It can transform the non-electricity or electromagnetic quantity into the desired electric signal through the change of the positional relationship between the sensor and the object, so as to achieve the purpose of control or measurement.
Motion Sensor Control Switch,Photoelectric Switch Sensors,Plug In Photoelectric Switch,Magnetoelectric Proximity Switches
Changchun Guangxing Sensing Technology Co.LTD , https://www.gx-encoder.com